Evaluating Impact of Incorporating Pediatric Clinical Practice Guidelines for Management of Infectious Diseases into an Electronic Application (Firstline)
Emily K Black ¹𝄒², Holly MacKinnon ¹, Jeannette Comeau ¹𝄒², Caroline King ³, Kathryn L Slayter ¹𝄒²
¹ Dalhousie University, ² IWK Health, ³ Nova Scotia Health
Background
- In 2017, IWK Health incorporated guidelines for infectious syndromes into an electronic App (Firstline)
- Healthcare providers in Nova Scotia identified the electronic App as a facilitator to improving antimicrobial use
Study Objectives
To compare antimicrobial prescribing before and after implementation of the electronic App (Firstline)
Methods
- Quasi-experimental design (Retrospective chart review before and after implementation of the App with an interrupted time series analysis)
- Pediatric patients who received an empiric antimicrobial agent for a suspected or confirmed infection listed in the App while admitted to hospital were included
- Empiric antimicrobial prescribing was assessed by two members of the research team using a previously developed checklist and considering patient specific factors (Checklist developed with input from experts using the Delphi Method)
Disclosures and Acknowledgements
Authors of this study have no conflicts of interest to disclose. This study was funded by the Dalhousie University Pharmacy Endowment Fund
Baseline Characteristics
Table 1: Baseline Characteristics
| Characteristic | Pre-Intervention (n=238) | Post-Intervention (n=243) |
|---|---|---|
| Age | ||
|
< 2 months |
22.37% |
22.37% |
|
2 months to 3 years |
25.74% |
24.69% |
|
3 years - 5 years |
10.13% |
15.23% |
|
6 years to 13 years |
34.14% |
41.15% |
|
> 13 years |
6.75% |
7.82% |
| Sex | ||
|
Female |
44.49% |
44.86% |
|
Male |
55.51% |
55.14% |
Results
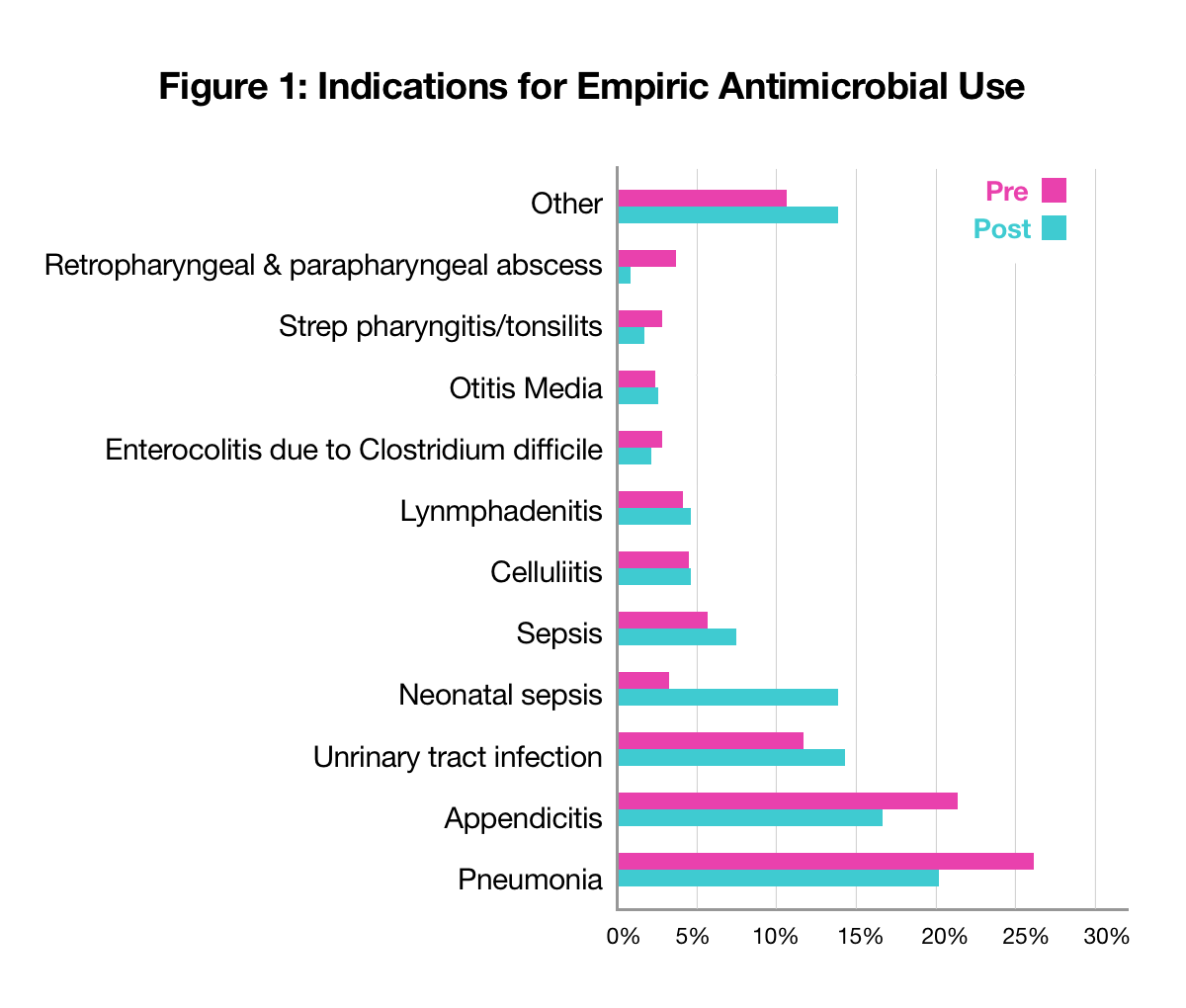
- 238 patients were included in the pre- intervention arm and 243 patients in the post-intervention arm (Table 1, Figure 1)
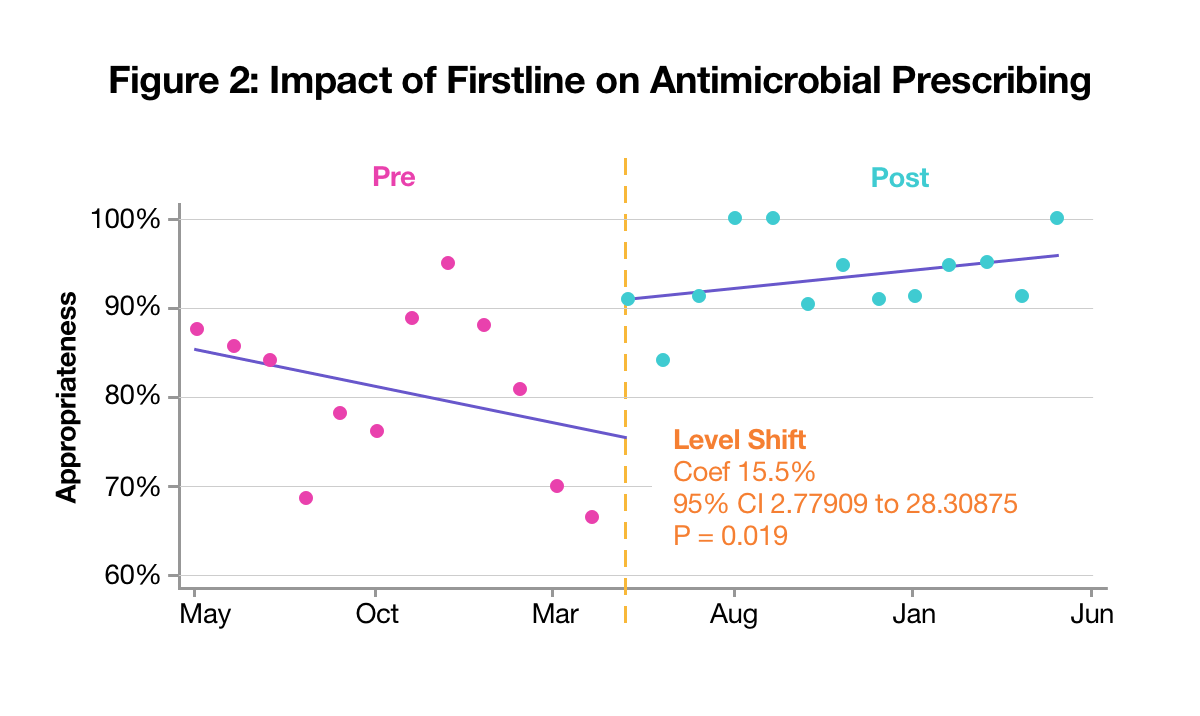
- The electronic App (Firstline) showed an immediate 15.6% improvement in antibiotic prescribing (Figure 2)
Limitations
- Generalizability
- Retrospective design
- Differences in patient population
Conclusion
- Antimicrobial prescribing improved after implementation of an electronic App (Firstline)
- Further research to explore impact of the electronic App on specific infectious syndromes and on patient outcomes is needed
Study Contact: [email protected]